Alzheimer's disease, a neurodegenerative disease common in the elderly, is characterized by the formation of beta-amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles in the brain. In recent years, with the deepening of scientific research, treatment methods around neurotransmitters have become a new focus of Alzheimer's disease research.
Key points
- Neurotransmitters play a vital role in Alzheimer's disease.
- Studies have revealed that the levels of neurotransmitters in the brains of patients with Alzheimer's disease have changed significantly, especially the reduction of acetylcholine, which is closely related to cognitive dysfunction.
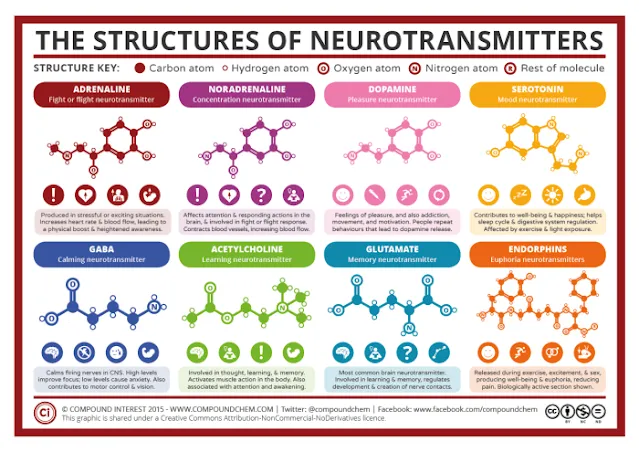
- In addition to acetylcholine, other neurotransmitters such as glutamate, dopamine, and 5-hydroxytryptamine also play an important role in the disease.
Table of Contents
- What are the basics of neurotransmitters?
- Which neurotransmitters are affected by Alzheimer's disease?
- How do neurotransmitters affect Alzheimer's disease?
- Research and treatment related to neurotransmitters
What are the basics of neurotransmitters?
Neurotransmitters, chemical messengers in the nervous system, are responsible for transmitting information between neurons or between neurons and muscles. The release and reception of neurotransmitters occurs in a tiny space called the synaptic cleft. They can be classified as excitatory, inhibitory, or regulatory based on their effects on the receiving neuron, thereby regulating various functions in the brain.
In the course of Alzheimer's disease, the most concerned neurotransmitter acetylcholine has a significant decrease in concentration in the patient's brain, affecting memory and learning ability. In addition, changes in other neurotransmitters such as glutamate, dopamine, and serotonin also have an important impact on the development of the disease.
How do neurotransmitters affect Alzheimer's disease?
In Alzheimer's disease, a significant reduction in acetylcholine causes atrophy of memory function areas, and as the disease progresses, other areas of the brain are gradually affected. Insufficient neurotransmitter levels may lead to symptoms such as depression, changes in appetite, and sleep disorders.
Neurotransmitter-Related Research and Treatment
More than a century has passed since Dr. Alzheimer observed Alzheimer's disease in "August Det" in 1901, but there are still no metabolic-based therapies to prevent Alzheimer's disease, although some therapies may temporarily relieve symptoms. The FDA has approved three AChEIs, one NMDA antagonist, and one combination of an AChEI and NMDA antagonist. One drug, tacrine, has been discontinued due to hepatotoxicity in AD patients.
references
Therapeutics of Neurotransmitters in Alzheimer’s Disease


Comments
Post a Comment